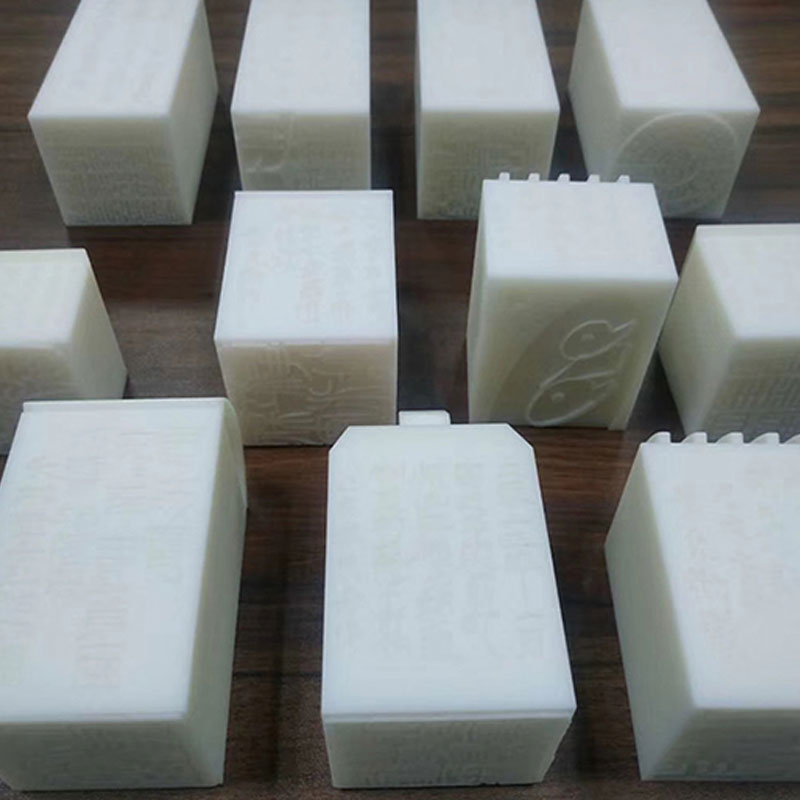
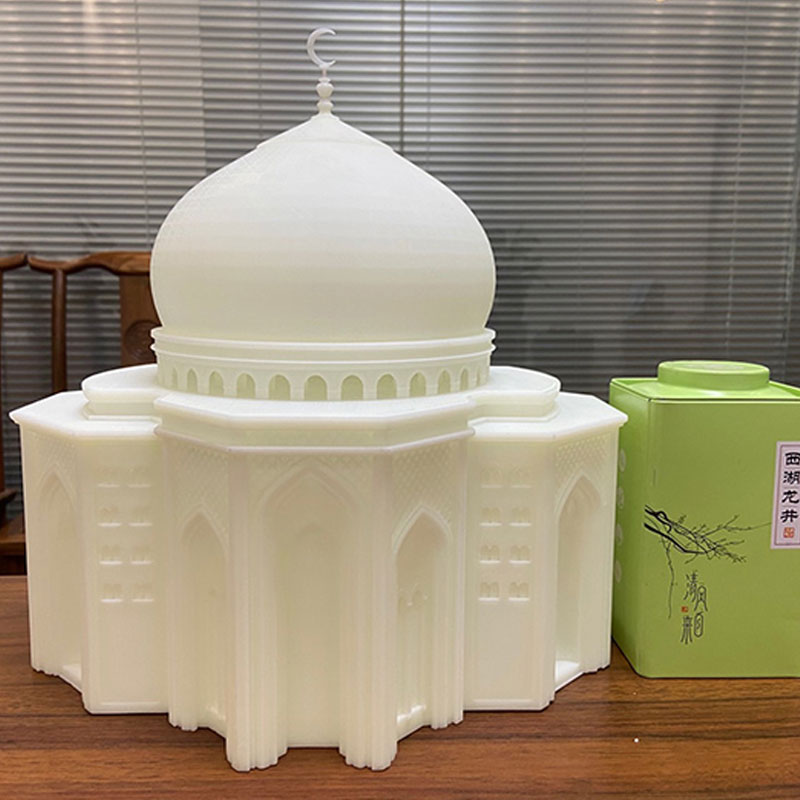
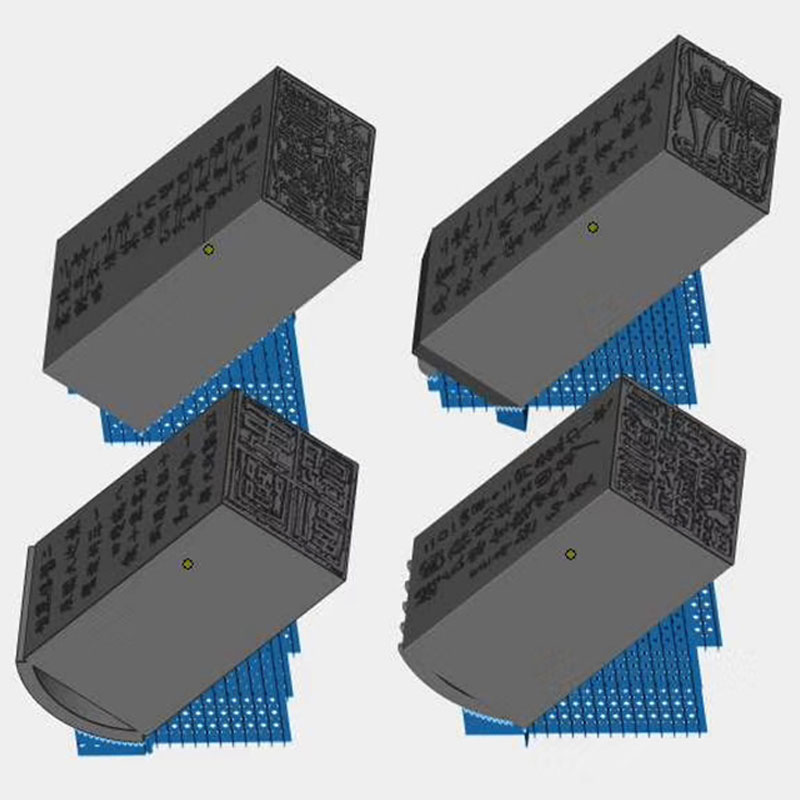
Custom Stamps
- – Material: White Resin
- – Accuracy: 0.2mm
- – Process: White Resin 3D Printing
- – Finlishing: Custom
- – Process: SLS 3D Printing
- – Easy to clean and maintain
- – High brightness and good appearance
- – Excellent quality and toughness
- – Great performance and durability
The fabrication of 3D printed products is based on the design files. There are some details and features that always need to be taken into account when designing a 3D printing part, but the best result varies depending on the different 3D printing services.Wonder Tech have a wide range of process and materials to choose from, each with its own benefits and applications.
Specifications
Parameter
Material
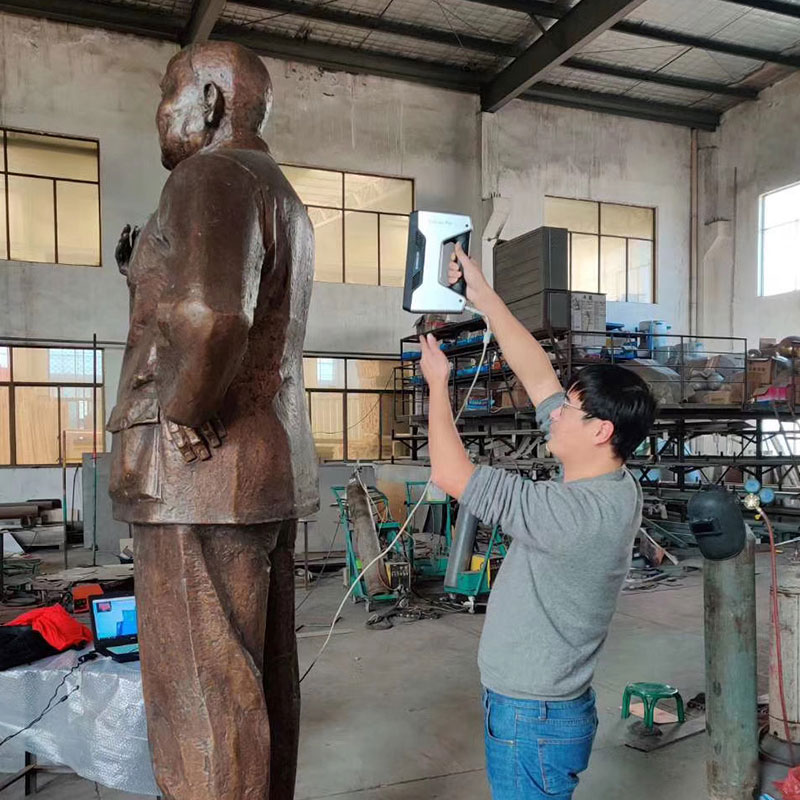
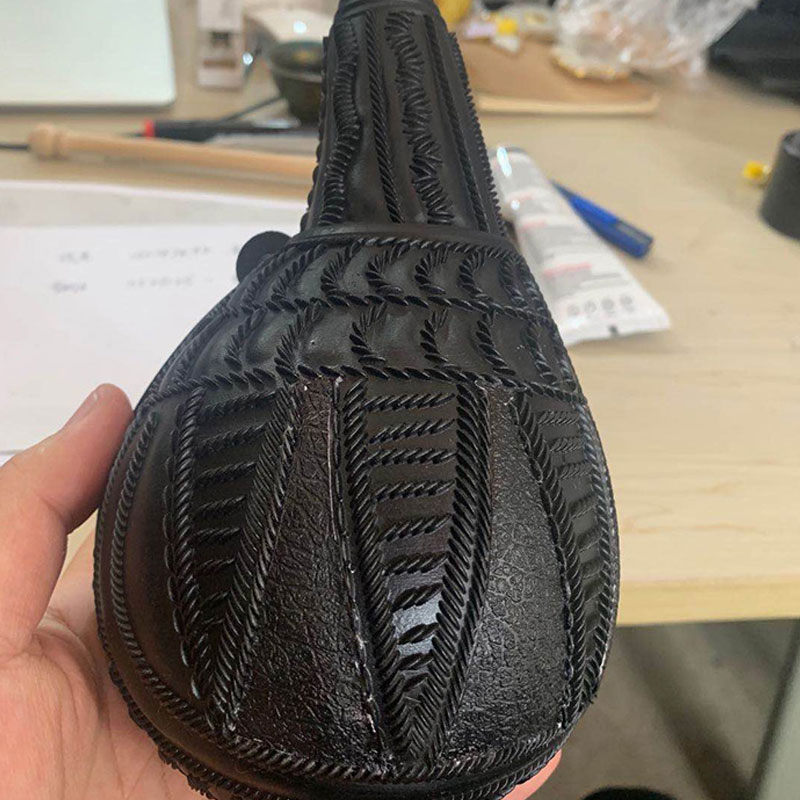
The client wanted a customised seal based on a manuscript. Once the manuscript was obtained the lines were first extracted, the vector lines were entered into the modelling software and the manuscript was placed on the different sides of the stamp to meet the client’s needs. After processing to meet the printing requirements the finished product was obtained.
Customer Supplied Seal Effect

World-Class Custom Stamps Via Images 3D Printing Services
Wonder Tech is dedicated to providing game-changing solutions- high-performance solutions and faster 3D Printing Custom Stamps Services Via Images with flexible designs.
We have brought nearly 20 years of materials and manufacturing expertise to every layer of your 3D products to help you in unlocking every dimension of 3D printing techniques.
3D Printing Technology And Material Table
At present, the commonly used 3D printing technologies include Multi Jet Fusion(MJF), Selected Laser Sintering(SLS), Stereolithography(SLA), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), and Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS).
| Cumulative Technology | Basic Material |
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | Thermoplastics, eutectic system metals, edible materials |
| Electronic Beam Freeform Fabrication (EBF) | Almost any alloy |
| Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) | Almost any alloy |
| Electron Beam Melting (EBM) | Titanium alloy |
| Selective Laser Melting (SLM) | Titanium alloy, cobalt chromium alloy, stainless steel, aluminum |
| Selective Heat Sintering (SHS) | Thermoplastic powder |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Thermoplastic, metal powder, ceramic powder |
| Polypropylene (PP) | plaster |
| Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) | Paper, metal film, plastic film |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Light hardening resin |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP) | Light hardening resin |
Our Quality Promise
Have an idea? have a napkin sketch? From proof of concept to functional tools for the manufacturing floor, 3-di.com has multiple 3D printing technologies at our disposal to help you bring your design to life. Contact us today!Send your files to reiceve a quote. Accepted file types: Hi-Res .stl, .sldprt. .step, .jpg, .pdfInspection reports included with every orderAccuracy up to 0.01mm, maximum size 1500mm100% visual inspection for every part Highly vetted 3D printing partnersMaterial certifications availableQuality guaranteed. If your parts aren’t made to spec, we’ll make it right.Over 100 machines running 24 hours a dayMore than 60 experienced masters
3D Printing Part Sizes
| FDM | 200 x 200 x 200 mm for desktop printers, up to 900 x 600 x 900 mm for industrial printers |
| SLA | 145 x 145 x 175 mm for desktop printers, up to 1500 x 750 x 500 mm for industrial printers |
| SLS | 300 x 300 x 300 mm, up to 750 x 550 x 550 mm |
| DMLS/SLM | 250 x 150 x 150 mm, up to 500 x 280 x 360 mm |
| MJF | 380 x 285 x 380 mm |
Dimensional Accuracy In 3D Printing
The dimensional accuracy refers to how accurate the size and form of the printed part are compared to that in the CAD design. Factors that affect dimensional accuracy include material quality, equipment, post-processing, and more. Dimensional tolerance, shrinkage, and support requirements are three key elements to measuring dimensional accuracy. Below are the dimensional tolerance of different 3D processes.
| FDM dimensional tolerance | prototyping (desktop):±0.5% (lower limit:±0.5 mm), industrial:±0.15% (lower limit:±0.2 mm) |
| SLA dimensional tolerance | prototyping (desktop):±0.5% (lower limit:±0.10 mm) industrial:±0.15% (lower limit:±0.01 mm) |
| SLS/MJF dimensional tolerance | ±0.3% (lower limit:±0.3 mm) |
Layer Height In 3D Printing
Layer height is a measurement of the amount of material extruded by the printer’s nozzle for each layer of your part. It is measured in microns or millimeters. The selection of layer height is important for some 3D printing technologies, such as SLA and FDM. Below are the typically applied layer height for different processes.
- – FDM: 50 – 400 μm
- – SLA: 25 – 100 μm
- – SLS: 80 – 120 μm
- – MJF: 80 μm
- – DMLS/SLM: 30 – 50 μm
3D printing and prototyping have advanced development in recent years. With these improvements, metal 3D printing has become a possibility. Metal 3D printing is used in a variety of sectors. Companies that use metal 3D printing are discovering that 3D printing complicated metal parts in low quantities is considerably more cost-effective than traditional methods of production. Metal 3D printed items are cheaper and have a wider range of material alternatives. Aluminum is a popular metal for 3D printing since it is both sturdy and lightweight. Steel is another extensively used material that is perfect for industrial applications due to its strength, good polish, and temperature tolerance. Metal 3D printing is utilized in a wide range of sectors for a variety of purposes. Functional prototypes, end-use parts, Jigs, tooling, and fixtures are some of the applications.
| Metals | Applications |
|---|---|
| Stainless steel | Utensils, cookware, and other items that could ultimately come into contact with water |
| Bronze | Vases and other fixtures |
| Gold | Rings, earrings, bracelets, and necklaces |
| Nickel | Coins |
| Aluminum | Thin metal products |
| Titanium | Strong, solid fixtures |
3D Printing Plastic Materials Guide
Wonder Tech provides plastic 3D printing services with constantly high efficiency and quick turnaround. Advanced 3D printers and optimal materials allow us to ensure both cheap prices and premium quality.
| Plastics | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Tough, strong, durable, heat-resistant, cost-effective, flexible, reusable, not biodegradable | Car bodies, appliances, and mobile phone cases |
| PLA | Easy to work with, environmentally friendly, biodegradable, available in resin and filament with a variety of colors | Food packaging, biodegradable medical devices and implants |
| PVA | Water-soluble | Often use to create a support structure for portions of a product that may warp or collapse |
| PP | Affordable, chemical resistant, flammable, and degrades with UV light | Household containers, lab equipment, and textiles |
| Nylon/PA | Strong, lightweight, durable, heat and impact-resistant, but not resistant to strong acids and bases | Applications that require high mechanical properties and functional prototypes |
| PEI | Can withstand high heat | Injection mold tools and heat-resistant components |
| PC | Heat resistant up to 135 °C, durable, impact and shatter resistant, moderately flexible, transparent, electrically non-conductive | Prototype windows and other clear products |
| PMMA/Acrylic | Good impact strength, comparable clarity, and UV absorption properties | Automobile headlights, commercial aquariums and other alternatives to glass |
| CPVC | High heat distortion temperature, chemical inertness, dielectric, and flame and smoke properties | Chemical processing, power generation, semiconductor, wastewater treatment |
| PEEK | Wear-resistant, good weight-to-strength ratio, high thermomechanical properties | Medical custom-made implants, devices, aerospace and automotive parts |
| PETG | High impact resistance, excellent chemical and moisture resistance | Compliant mechanisms, water bottles, electronic enclosures |
| TPU | Flexible, abrasion-resistant, resistant to impacts and many chemicals | Sporting goods, aerospace and automotive |
| PETP/Ertalyte | High dimensional stability, mechanical strength, low moisture absorption, physiologically inert | Thin films, containers for liquid drinks |